Methodology
1. Gray scale the image
A grayscale image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample representing only an amount of light
| Linear Luminance | let lightness = 0.2126 * pixels[i] + 0.715 * pixels[i+1] + 0.0722 * pixels[i+2]; | $Y = 0.2126 R + 0.7152 G + 0.0722 B $ |
| Luma | let lightness = parseInt(pixels[i]*.299 + pixels[i + 1]*.587 + pixels[i + 2]*.114); | $Y = 0.299 R + 0.587 G + 0.114 B $ |
let lightness = parseInt(3*pixels[i] + 4*pixels[i + 1] + pixels[i + 2] >>> 3); | $Y = 0.2627 R + 0.6780 G + 0.0593 B $ |
1. b Convert to a binary image using a threshold
const imageData = ctx.getImageData(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
const data = imageData.data;
// Convert to grayscale and detect edges
const grayscale = [];
const edges = [];
for (let y = 0; y < canvas.height; y++) {
for (let x = 0; x < canvas.width; x++) {
const i = (y * canvas.width + x) * 4;
const r = data[i], g = data[i + 1], b = data[i + 2];
// Simple grayscale conversion
const gray = 0.3 * r + 0.59 * g + 0.11 * b;
grayscale.push(gray);
// Simple edge detection (using a threshold)
if (gray < 240) { // Threshold value to detect black borders (128 Default)
edges.push({ x, y });
}
}
}2. FloodFill
The algorithm looks for all nodes in the array that are connected to the start node by a path of the target color and changes them to the replacement color.
.gif)
The algorithm use a stack (or queue) to prevent stack overflow that would happen with recursion.
Pseudocode
Flood-fill (node):
1. Set Q to the empty queue or stack.
2. Add node to the end of Q.
3. While Q is not empty:
4. Set n equal to the first element of Q.
5. Remove first element from Q.
6. If n is Inside:
Set the n
Add the node to the west of n to the end of Q.
Add the node to the east of n to the end of Q.
Add the node to the north of n to the end of Q.
Add the node to the south of n to the end of Q.
7. Continue looping until Q is exhausted.
8. Return.2. Boundary tracing algorithm
- Locate a boundary pixel: Start at a pixel known to be part of the border of the desired area.
- Contour tracing: Begin tracing by moving to one of the neighboring pixels with the same color, following the boundary of the shape.
- Moore-neighbor algorithm:
- Move clockwise or counterclockwise, checking the 8 neighboring pixels, and follow the path formed by pixels of the same color.
- If you reach a branch, continue following the border (since it is the same color).
- Stop when you return to the starting pixel: Once you've fully traced the boundary.
- Suzuki and Abe Algorithm (Topological Structural Analysis of Digitized Binary Images)
- Best for: Binary images with multiple contours, including nested contours (like holes within objects).
- How it works: It efficiently finds contours in binary images by following pixel chains. It's implemented in many image-processing libraries (like OpenCV) as cv.findContours.
4. Calculating the area
Shoelace forumla
[Wiki] The shoelace formula, also known as Gauss's area formula and the surveyor's formula, is a mathematical algorithm to determine the area of a simple polygon whose vertices are described by their Cartesian coordinates in the plane. Trapezoid Formula
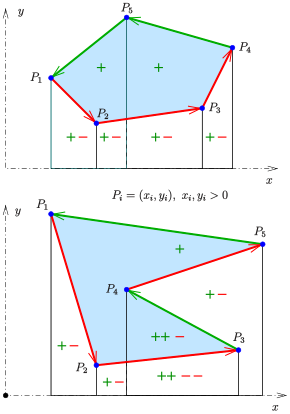
function ShoelaceAlgorithm(){
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
sum += (clicks[i + 1].x + clicks[i].x) * (clicks[i + 1].y - clicks[i].y)
}
sum += (clicks[0].x + clicks[n - 1].x) * (clicks[0].y - clicks[n - 1].y)
return Math.abs(sum / 2);
}5. Find point inside
CanvasRenderingContext2D.isPointInPath()Ray casting algorithm
One simple way of finding whether the point is inside or outside a simple polygon is to test how many times a ray, starting from the point and going in any fixed direction, intersects the edges of the polygon. Wiki
// Point-in-polygon algorithm (Ray-casting algorithm)
function isPointInPolygon(x, y, polygon) {
let isInside = false;
const vertices = polygon.vertices;
const n = vertices.length;
for (let i = 0, j = n - 1; i < n; j = i++) {
const xi = vertices[i].x, yi = vertices[i].y;
const xj = vertices[j].x, yj = vertices[j].y;
const intersect = ((yi > y) !== (yj > y)) &&
(x < (xj - xi) * (y - yi) / (yj - yi) + xi);
if (intersect) isInside = !isInside;
}
return isInside;
}function point_in_polygon(point, polygon) {
const num_vertices = polygon.length;
const x = point.x;
const y = point.y;
let inside = false;
let p1 = polygon[0];
let p2;
for (let i = 1; i <= num_vertices; i++) {
p2 = polygon[i % num_vertices];
if (y > Math.min(p1.y, p2.y)) {
if (y <= Math.max(p1.y, p2.y)) {
if (x <= Math.max(p1.x, p2.x)) {
const x_intersection = ((y - p1.y) * (p2.x - p1.x)) / (p2.y - p1.y) + p1.x;
if (p1.x === p2.x || x <= x_intersection) {
inside = !inside;
}
}
}
}
p1 = p2;
}
return inside;
}References
[1] (Boundary tracing)(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boundary_tracing)
[2] (ContourTracing)(https://www.imageprocessingplace.com/downloads_V3/root_downloads/tutorials/contour_tracing_Abeer_George_Ghuneim/moore.html)
[3] (Point in polygon)(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Point_in_polygon)
[4] (Shoelace formula)(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shoelace_formula)
